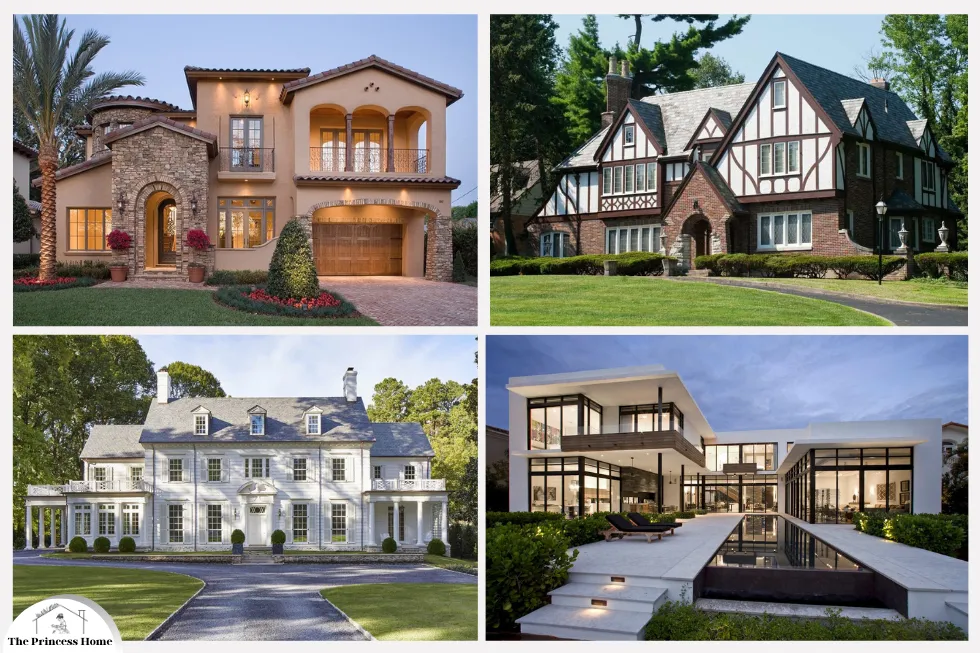
Choosing the right color scheme for a building is a critical aspect of architectural design. Consequently, the colors used can influence the overall aesthetic, evoke specific moods, and enhance the architectural features. Moreover, different architectural styles have their own unique characteristics and historical contexts. Therefore, these factors should be considered when selecting colors.
In this article, we will explore the principles and guidelines for selecting appropriate color schemes for various architectural styles
Selecting appropriate color schemes for different architectural styles involves understanding the aesthetic principles, historical context, and cultural influences associated with each style.
Understanding Architectural Styles:
Before delving into color selection, it’s essential to understand the key features and characteristics of different architectural styles. so each style has its own set of design principles, materials, and cultural influences that shape its appearance. and the symmetrical facades of colonial buildings to the ornate details of Victorian homes and the sleek lines of modern architecture, each style offers distinct opportunities for color exploration.
Here are some general guidelines for selecting color schemes for several architectural styles:
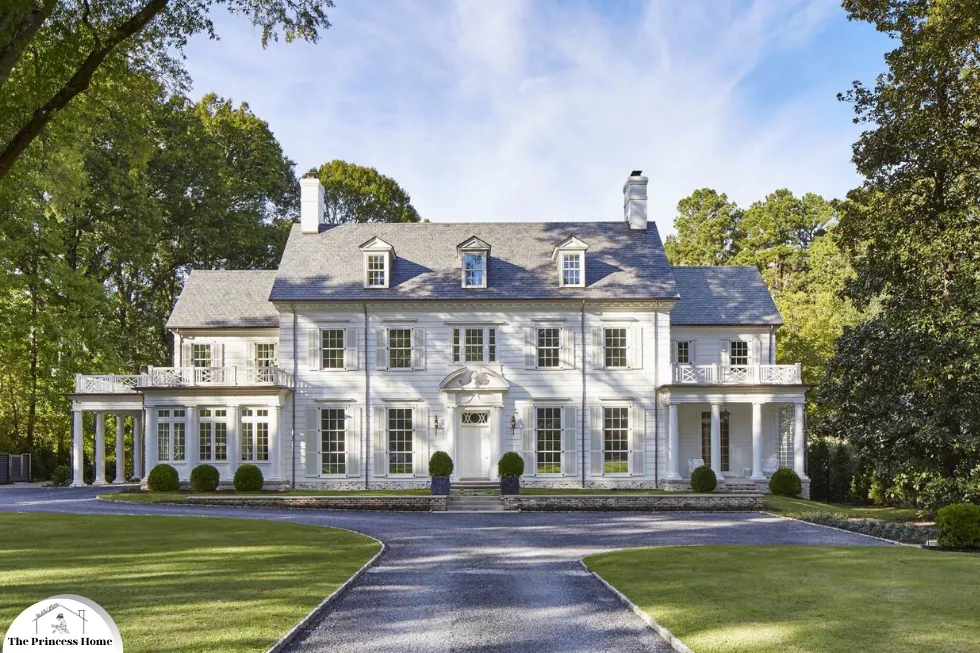

1.Colonial Architecture:
Colonial architecture, which prevails in regions with colonial histories such as North America and parts of Asia, features symmetrical facades, traditional elements, and a sense of orderliness. When selecting color schemes for colonial-style buildings, it’s essential to choose classic colors that reflect the elegance and simplicity of the style. Whites, creams, and light grays are popular choices for the main body of the building, while accents in navy blue, forest green, or burgundy can add depth and sophistication.
Colonial architecture refers to the architectural styles that were prevalent during the period of colonialism, particularly during the expansion of European powers from the 15th to the 19th centuries. It encompasses a wide range of styles influenced by the colonizing nation’s culture, as well as the local climate, materials, and traditions of the colonized regions.
Common features of colonial architecture include:
1.Symmetry: Buildings often exhibit symmetrical designs, with evenly spaced windows and doors.
2.Columns and Pillars: Many colonial buildings feature columns and pillars, which are often inspired by classical Greek or Roman architecture.
3.Verandas and Porches: Due to the warm climates of many colonial regions, buildings often have verandas or porches, providing shaded outdoor spaces.
4.Stucco or Stone Facades: Exterior walls are typically made of stucco or stone, providing durability and protection from the elements.
5.Pitched Roofs: Roof styles vary, but pitched roofs are common in colonial architecture, allowing for efficient rainwater drainage.
5.Shutters: Decorative shutters are often found on windows, providing both aesthetic appeal and protection from storms.
6.Courtyards and Gardens: Many colonial buildings are centered around courtyards or feature lush gardens, blending indoor and outdoor spaces.
7.Adaptation to Local Materials and Climate: Colonial architecture often incorporates local materials and building techniques, adapted to suit the climate and environment of the colonized region.
Examples
Colonial architecture exists in regions such as Latin America, the Caribbean, Africa, Southeast Asia, and parts of North America, where European powers established colonies and left lasting architectural legacies.
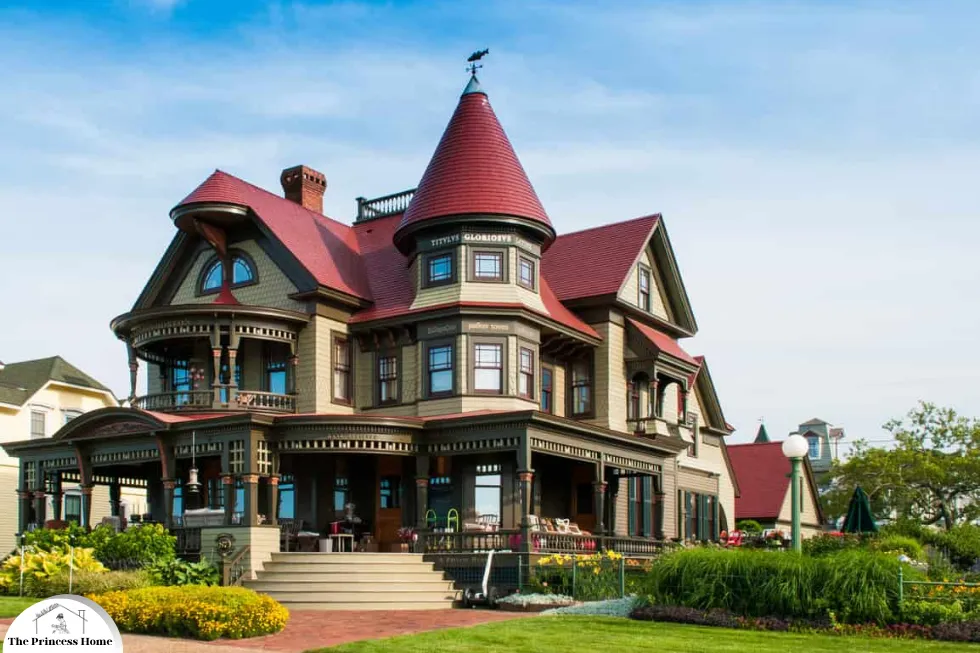

2.VictorianArchitecture:
Ornate details and vibrant colors characterize Victorian architecture. Choose rich hues like deep reds, purples, and blues for the exterior, paired with contrasting trim in lighter shades or gold accents so earthy tones such as olive green or mustard yellow can also complement Victorian homes.
Victorian architecture refers to the architectural styles that were popular during the reign of Queen Victoria of England, from 1837 to 1901. and It was a period of significant architectural diversity, with a wide range of styles influenced by the social, political, and technological changes of the time.
Key features of Victorian architecture include:
1. Eclecticism: Victorian architecture exhibits an eclectic mix of styles, often blending elements from earlier architectural movements such as Gothic Revival, Italianate, Queen Anne, and Romanesque Revival.
2.Ornamentation: Buildings from this era are typically highly ornamented, featuring intricate details such as decorative trim, carved stonework, and elaborate moldings.
3.Steeply Pitched Roofs: Many Victorian buildings have steeply pitched roofs with intricate gables, turrets, and dormer windows, adding to their dramatic appearance.
4.Bay Windows: Bay windows are a common feature of Victorian architecture, providing additional space and allowing more natural light into the interior.
5.Textured Facades: Victorian buildings often have textured facades, with a variety of materials such as brick, stone, and wood used to create visual interest.
6.Colorful Paint Schemes: Victorians were fond of using bold and vibrant colors to paint their homes, often with contrasting trim and accents.
7.Towers and Turrets: Many Victorian buildings include towers or turrets, adding vertical emphasis and creating a sense of grandeur.
8.Verandas and Porches: Like colonial architecture, Victorian buildings often feature verandas or porches, providing outdoor living spaces and adding to their picturesque appeal.
Examples
Victorian architecture can be found in cities and towns across the United Kingdom, as well as in former British colonies around the world. Notable examples include the Houses of Parliament in London, the Royal Exhibition Building in Melbourne, Australia, and the Painted Ladies of San Francisco, California.
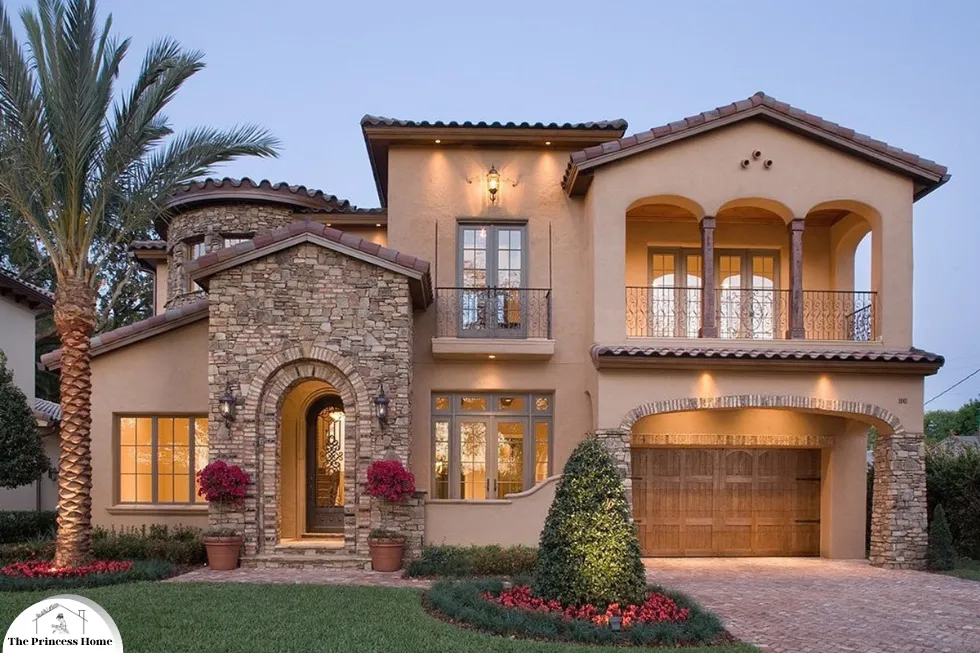

3.Mediterranean Architecture:
Mediterranean architecture is known for its warm and inviting aesthetic, inspired by the coastal regions of Southern Europe. For the exterior, consider earthy tones such as terracotta, ochre, or sandy beige to evoke the sun-drenched feel of the Mediterranean. Accents in shades of blue, reminiscent of the sea and sky, can add a refreshing touch. Additionally, incorporating elements like wrought iron details, clay roof tiles, and stucco finishes can further enhance the Mediterranean style of your home.
Mediterranean architecture refers to the architectural styles found in the regions surrounding the Mediterranean Sea, including countries such as Spain, Italy, Greece, Turkey, and Morocco. It is characterized by its timeless beauty, functionality, and harmony with the natural environment. Mediterranean architecture has evolved over centuries, influenced by various civilizations and cultural exchanges in the region.
Key features of Mediterranean architecture include:
1.Whitewashed Walls: Many Mediterranean buildings have whitewashed or brightly colored exterior walls, which help to reflect sunlight and keep interiors cool in hot climates.
2.Terracotta Roof Tiles: Red or terracotta-colored roof tiles are a common feature of Mediterranean architecture, providing both insulation and a distinctive aesthetic.
3.Arched Doorways and Windows: Arches are a prominent architectural element in Mediterranean design, adding elegance and character to buildings. Arched doorways and windows are often adorned with decorative details.
4.Courtyards and Patios: Mediterranean architecture often includes interior courtyards or outdoor patios, serving as private retreats for relaxation and socializing.
5.Wrought Iron Details: Builders frequently use ornate wrought ironwork for gates, railings, and window grilles, adding a touch of elegance and security to Mediterranean homes.
6.Stone and Stucco Construction: Many Mediterranean buildings blend seamlessly with the natural landscape and create a sense of harmony with the surroundings by constructing them from local stone or stucco.
7.Mosaic Tile Accents: Builders often use colorful mosaic tiles to decorate floors, walls, and fountains, adding visual interest and beauty to both interior and exterior spaces.
8.Shaded Outdoor Spaces: To cope with the Mediterranean climate’s intense sun and heat, buildings often feature shaded outdoor areas such as pergolas, covered verandas, or loggias, allowing residents to enjoy the outdoors comfortably.
9.Mediterranean Gardens: Landscaping is an integral part of Mediterranean architecture, with lush gardens filled with aromatic herbs, citrus trees, and flowering plants contributing to the overall ambiance.
Examples
Mediterranean architecture dots historic cities like Barcelona, Rome, Athens, and Istanbul, as well as picturesque coastal villages throughout the Mediterranean region. These buildings showcase the timeless elegance and practical design principles that have made Mediterranean architecture beloved around the world.

4.Modern Architecture:
Modern architecture embraces clean lines, minimalism, and a focus on functionality. For the exterior, consider using a palette of neutral colors such as white, gray, or taupe to create a sleek and contemporary look. Accents in black or metallic tones can add contrast and sophistication. Additionally, incorporating large windows, geometric shapes, and asymmetrical designs can further enhance the modern aesthetic of your home.
Modern architecture refers to the architectural styles that emerged in the late 19th and 20th centuries, characterized by a departure from traditional design principles and a focus on innovation, functionality, and the use of new materials and construction techniques. Modern architecture reflects the spirit of its time, embracing technological advancements, social changes, and a desire for simplicity and efficiency.
Key features of modern architecture include:
1.Simplicity and Minimalism: Modern buildings often feature clean lines, geometric shapes, and minimal ornamentation, emphasizing simplicity and clarity of form.
2.Use of Industrial Materials: Modern architects embraced industrial materials such as steel, glass, and concrete, allowing for innovative structural designs and open, flexible spaces.
3.Open Floor Plans: Modern buildings often have open floor plans, with large, uninterrupted interior spaces that flow seamlessly from one area to another, blurring the boundaries between rooms.
4.Integration of Indoor and Outdoor Spaces: Modern architecture emphasizes the connection between indoor and outdoor environments, with features such as floor-to-ceiling windows, sliding glass doors, and outdoor living areas.
5.Flat Roofs and Horizontal Emphasis: Many modern buildings feature flat or low-pitched roofs, emphasizing horizontal lines to create a sense of horizontality and stability.
6.Innovative Structural Systems: Modern architects developed new structural systems that allowed for greater flexibility in design, including cantilevered structures, curtain walls, and reinforced concrete.
7.Emphasis on Functionality: Modern architecture prioritizes functionality and efficiency, with buildings designed to meet the needs of their occupants in terms of comfort, usability, and sustainability.
8.Experimentation and Innovation: Modern architects gained recognition for their willingness to experiment with new ideas and technologies, pushing the boundaries of what was possible in terms of design and construction.
9.Adaptive Reuse and Sustainability: In recent decades, modern architecture has increasingly focused on adaptive reuse and sustainable design principles, repurposing existing buildings and incorporating eco-friendly materials and practices.
Examples
of modern architecture include iconic buildings such as the Bauhaus School in Germany, the Fallingwater House by Frank Lloyd Wright in the United States, the Sydney Opera House in Australia, and the Guggenheim Museum in Bilbao, Spain. These buildings showcase the diversity and innovation of modern architectural design, as well as its enduring influence on the built environment.
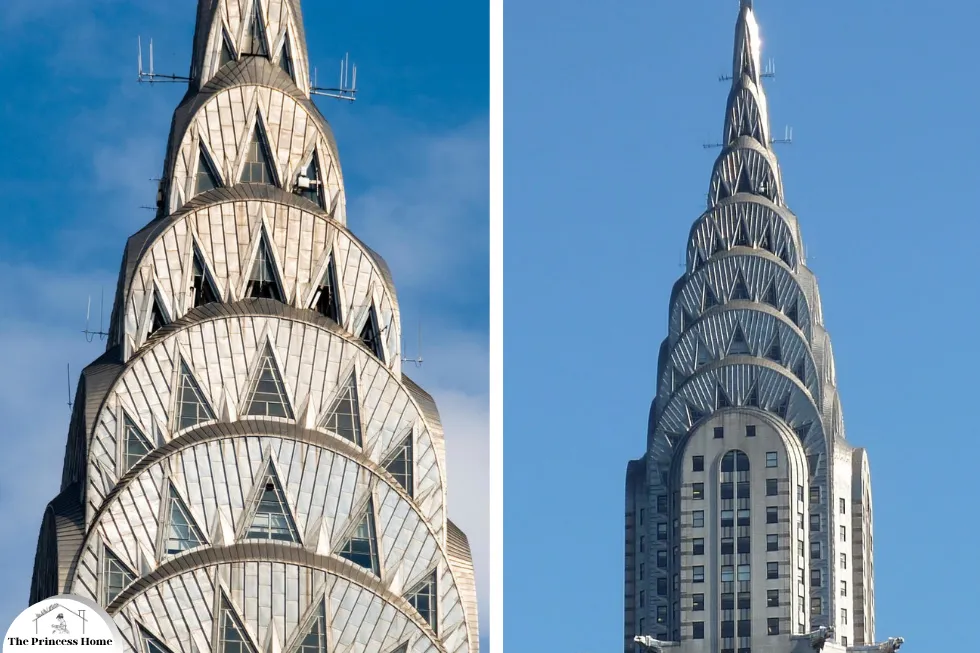

5.Art Deco Architecture:
Its bold geometric shapes, lavish ornamentation, and glamorous aesthetic characterize Art Deco architecture. For the exterior, consider using colors like rich jewel tones such as emerald green, sapphire blue, or ruby red to evoke the opulence of the Art Deco era. Contrast these vibrant hues with accents in metallic tones such as gold, silver, or bronze for added drama. Additionally, incorporating geometric patterns, streamlined forms, and decorative elements like chevrons or sunbursts can further enhance the Art Deco style of your home.
Art Deco architecture refers to a distinctive architectural style that flourished during the 1920s and 1930s, particularly in the period between the two World Wars. Its bold geometric shapes, sleek lines, vibrant colors, and decorative motifs inspired by modern technology and the machine age characterize it. Art Deco architecture exudes a sense of glamour, luxury, and optimism, reflecting the spirit of the Jazz Age and the Roaring Twenties.
Key features of Art Deco architecture include:
1.Geometric Shapes: Art Deco buildings often feature geometric shapes such as zigzags, chevrons, sunbursts, and stepped forms, creating dynamic and visually striking facades.
2.Sleek Lines: Art Deco design emphasizes horizontal and vertical lines, giving buildings a sense of streamlined elegance and modernity.
3.Ornamental Details: Art Deco buildings adorn their facades with decorative elements such as stylized motifs, sunbursts, floral patterns, and geometric reliefs, adding richness and texture.
4.Use of Luxurious Materials: Art Deco architects preferred luxurious materials such as polished stone, marble, chrome, glass, and terracotta, using them to create lavish interiors and exterior details.
5.Symmetry and Asymmetry: While symmetry is often a hallmark of Art Deco design, architects also experimented with asymmetrical compositions, creating dynamic and visually intriguing buildings.
6.Vertical Emphasis: Many Art Deco skyscrapers and buildings feature vertical lines and setbacks, reflecting the era’s fascination with progress, technology, and urbanization.
7.Emphasis on Speed and Motion: Art Deco design often evokes a sense of speed, movement, and dynamism, with motifs inspired by airplanes, cars, trains, and other modes of transportation.
8.Influence of Ancient Cultures: Art Deco architects drew inspiration from a variety of sources, including ancient Egyptian, Aztec, Mayan, and African art and architecture, incorporating exotic motifs and decorative elements into their designs.
9.Integration of Decorative Arts: Art Deco architecture often integrates decorative arts such as sculpture, painting, and ceramics into its design, blurring the boundaries between architecture and other art forms.
Examples
Art Deco architecture graces cities around the world, boasting notable examples such as the Chrysler Building and Empire State Building in New York City, the Miami Beach Architectural District in Florida, the Palais de Tokyo in Paris, and the Marine Building in Vancouver, Canada.These buildings showcase the elegance, sophistication, and modernity of the Art Deco style, which continues to captivate admirers to this day.
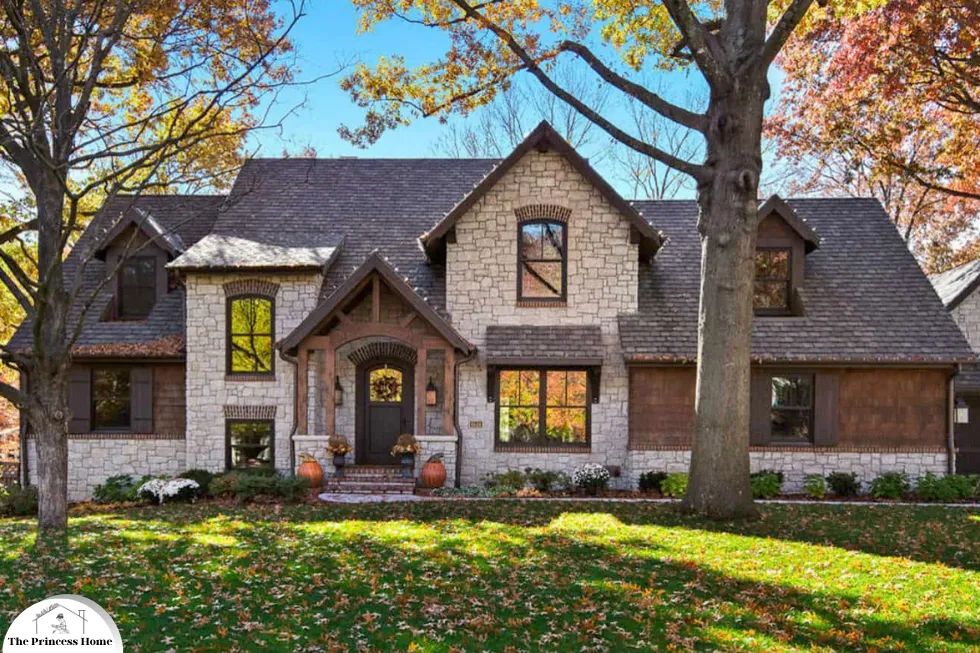

6.Craftsman Architecture:
Craftsman architecture distinguishes itself through its emphasis on craftsmanship, natural materials, and cozy atmosphere. For the exterior, choose earthy tones such as warm browns, deep greens, or rusty reds to reflect the natural surroundings. Accents in muted colors like cream or taupe can complement the Craftsman style beautifully. Consider incorporating natural wood elements such as exposed beams, shingles, or stone accents to add texture and warmth. Additionally, details like tapered columns, front porches with low-pitched roofs, and decorative brackets can enhance the charm of your Craftsman home.
Craftsman architecture, also known as Arts and Crafts architecture, emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as a reaction against the mass-produced, ornate designs of the Victorian era. It emphasizes craftsmanship, simplicity, and the use of natural materials, reflecting the principles of the Arts and Crafts movement. Homeowners seeking a cozy and welcoming environment favor Craftsman homes for their warmth, comfort, and connection to nature.
Key features of Craftsman architecture include:
1. Low-Pitched Gable Roofs: Craftsman homes typically feature low-pitched gable roofs with wide eaves, often supported by exposed rafters or decorative brackets.
2. Wide Front Porches: Many Craftsman homes have wide, covered front porches, providing outdoor living space and inviting neighbors to socialize.
3. Simple and Functional Floor Plans: Craftsman homes often have open, flowing floor plans with few interior walls, creating a sense of spaciousness and flexibility.
4. Emphasis on Natural Materials: Craftsman architecture emphasizes the use of natural materials such as wood, stone, and brick, both for exterior cladding and interior finishes.
5. Handcrafted Details: Craftsman homes showcase the skill and artistry of craftsmen through their handcrafted details, including built-in cabinetry, woodwork, and trim.
6. Horizontal Emphasis: Craftsman architecture often features horizontal lines and proportions, with elements such as low-pitched roofs, wide porches, and banded windows contributing to a sense of solidity and grounding.
7. Exterior Woodwork: Craftsman homes may feature exposed wood beams, decorative brackets, and tapered columns, adding texture and visual interest to their facades.
8. Integration with Nature: Craftsman architecture seeks to harmonize with the natural landscape, with features such as large windows, French doors, and outdoor living spaces connecting indoor and outdoor environments.
9. Earth-Toned Color Palette: Craftsman homes are typically painted in earthy, natural colors such as brown, green, and ochre, reflecting their connection to the natural world.
Examples
Craftsman architecture can be found throughout the United States, particularly in regions such as California, the Pacific Northwest, and the Midwest. Notable examples include the Gamble House in Pasadena, California, designed by Greene and Greene, and the Robie House in Chicago, Illinois, designed by Frank Lloyd Wright. These homes exemplify the timeless appeal and craftsmanship of Craftsman architecture, which continues to inspire homeowners and architects today.
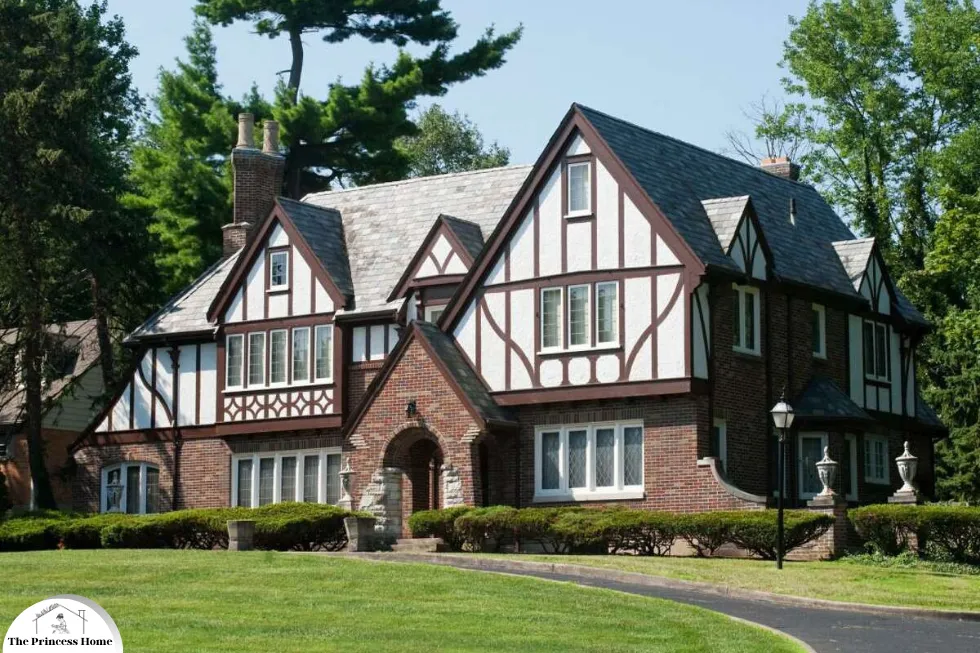

7.Tudor Architecture:
Tudor architecture is characterized by its distinctive timber-framed structures and intricate detailing. For the exterior, consider using a combination of rich, earthy tones such as dark brown, deep red, or olive green to highlight the exposed timber beams. Contrasting trim in lighter shades like cream or off-white can accentuate the Tudor style. Additionally, incorporating stone accents or brickwork can further enhance the rustic charm of your Tudor home. Tudor architecture often features steeply pitched roofs with cross gables, diamond-patterned leaded glass windows, and elaborate doorways, which contribute to its unique character and historical appeal.
Tudor architecture refers to the architectural style prevalent in England during the Tudor period, which spanned from the late 15th century to the early 17th century. This style is characterized by its distinctive features, including half-timbered construction, steeply pitched roofs, and elaborate decorative elements. Tudor architecture reflects the influence of medieval building traditions as well as Renaissance design principles.
Key features of Tudor architecture include:
1.Half-Timbered Construction: Tudor buildings often feature exposed timber framing, with the spaces between the wooden beams filled with plaster or brick infill. This half-timbered construction creates a striking visual contrast and adds texture to the facade.
2.Steeply Pitched Roofs: Tudor roofs are typically steeply pitched, with gables and dormer windows adding to their picturesque appearance. Thatched roofs were common in earlier Tudor buildings, while later examples often feature tiled or slate roofs.
3.Decorative Bargeboards and Finials: Tudor buildings are often adorned with decorative bargeboards and finials along the gables and rooflines, adding a whimsical and ornate touch to the facade.
4.Leaded Glass Windows: Tudor windows are typically small and multi-paned, with leaded glass casements adding to the historic charm of the building. Diamond-shaped or rectangular patterns are common in Tudor window design.
5.Tudor Archways: Tudor architecture is known for its distinctive Tudor arches, which are semi-circular or flattened arches with a pointed apex. These arches are often used for doorways, windows, and entrances.
6.Chimneys: Tudor buildings feature prominent chimneys, often with elaborate brickwork or decorative chimney pots. Multiple chimneys are sometimes clustered together for visual impact.
7.Symmetry and Proportion: Tudor buildings typically exhibit a sense of symmetry and proportion, with carefully balanced facades and well-proportioned windows and doorways.
8.Quoins and Bands of Brickwork: Some Tudor buildings feature decorative bands of brickwork or stone, known as “quoins,” which emphasize the corners of the building and add visual interest to the facade.
Examples
Tudor architecture can be found throughout England, particularly in historic cities such as London, Oxford, and Cambridge, as well as in rural villages and countryside estates. Notable examples include Tudor palaces such as Hampton Court Palace and country houses such as Anne Hathaway’s Cottage in Stratford-upon-Avon. These buildings showcase the enduring appeal and craftsmanship of Tudor architecture, which continues to be celebrated and emulated in modern-day architectural design.
Conclusion
When selecting color schemes for architectural styles, it’s essential to consider factors such as the building’s surroundings, climate, and historical significance. Experimenting with different combinations and consulting with a professional designer can help ensure that the chosen colors enhance the architectural features and create a cohesive, visually appealing aesthetic.
Here are some frequently asked questions related to selecting color schemes.
Q1: How do I choose the right color scheme for my colonial-style home?
A: For colonial architecture, consider classic colors like white, cream, or light gray for the main body of the building. Accents in colors such as navy blue, forest green, or burgundy can add depth and elegance.
Q2: What are some suitable color options for a Mediterranean-style building?
A: Mediterranean-style buildings often look great with warm, earthy tones such as terracotta, ochre, and sandy beige for the exterior. Consider adding accents of turquoise or cobalt blue for a touch of Mediterranean flair.
Q3: Can I use bold colors for a modern architectural style?
A: Absolutely! While modern architecture typically emphasizes neutral colors like white, gray, or taupe, you can incorporate bold accents in primary colors or muted tones to create visual interest without overwhelming the design.
Q4: Are there specific color choices that complement Tudor-style architecture?
A: Tudor architecture pairs well with earthy colors such as brown, tan, or dark green for the exposed timber framing. Consider creamy white or light beige stucco for the main body of the building, with accents in deep red or navy blue to add warmth and depth.
Q5: What colors should I avoid when selecting a color scheme for a craftsman-style home?
A: While craftsman-style homes often feature natural materials and earthy colors, it’s best to avoid overly bright or garish hues that might clash with the subdued aesthetic. Instead, opt for warm, muted tones that complement the architectural style.
Q6: Can I incorporate metallic colors into the color scheme of an Art Deco building?
A: Yes! Art Deco architecture often features metallic accents such as silver or gold. Consider incorporating these metallic hues alongside sophisticated colors like black, white, and bold jewel tones for a glamorous and striking aesthetic.
Q7: How important is it to consider the surrounding environment when choosing a color scheme for a building?
A: It’s crucial to consider the surrounding environment, including neighboring buildings, landscape features, and climate, when selecting a color scheme. Harmonizing with the surroundings can help ensure that the building blends in seamlessly and enhances its overall visual appeal.
These frequently asked questions and their answers can provide valuable guidance for individuals seeking to select appropriate color schemes for different architectural styles.